Principle
- When a magnet material is placed in the magnetic field, it always moves in the direction of strongest magnetic field.
- A synchro looks like as simple electrical motor and it works as variable transformer. Its operation depends upon electromagnetic induction.
Application
- Navy equipment
- Navy communication
- Under water detection system
- Navigation system
- Navy weapons
Construction
Stator
- The three-phase stator winding is embedded in the cylindrical structure of synchro similar to that of synchronous generator.
- The three-phase stator winding is placed at 120 degrees to each other.
Rotor
- Three are two types of rotors ( 1 ) salient pole and ( 2 ) wound rotor or drum type
- A dumbbell type construction is employed in the salient pole rotor whereas winding is done in the rotor slot of wound rotor.
- A single-phase supply is given to rotor via slip ring to rotor of synchro.
Working
- The synchro is a variable transformer.
- It consists of one primary winding in rotor and three stationary winding on stator which are displaced at 120 degree.
- As the primary winding is placed on rotor, it rotates at 360 degree.
- Let us understand operation of electromagnet before to understand synchro.
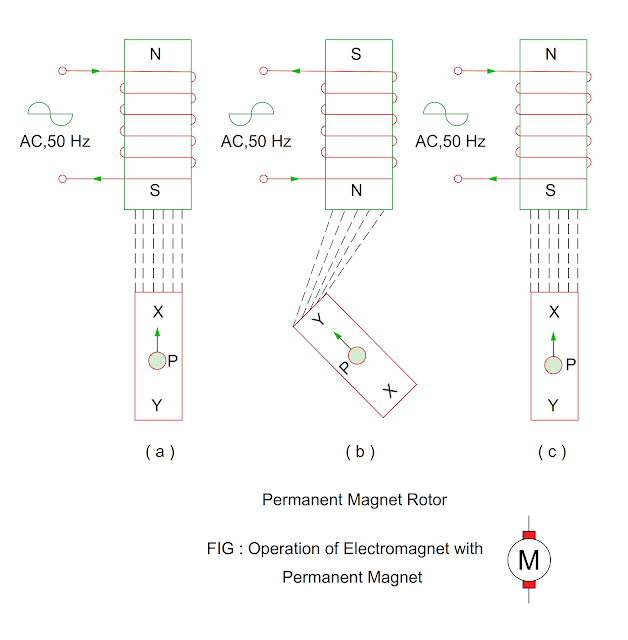
- One bar magnet is pivoted at point P in the field of electromagnet.
- A magnet lies in the direction of magnetic field as shown in figure ( a ). In which like poles repels whereas unlike poles attracts to each other.
- When a bar magnet is aligned in the direction of magnetic field, it is shortest path of magnetic force.
- When a force in the anti-clockwise direction is applied to the bar magnet, flux is distorting and length of magnetic field increases.
- Similarly, when a force on bar magnet released, bar magnet comes to its original position.
- When direction of current in the electromagnet is reversed, bar magnet rotates at 180 degree from its initial position ( Figure b ).
- These things keep in mind, a magnetic bar is placed in the three-phase winding or three electromagnet S1, S2 and S3.
- The three-phase winding is displaced at 120 degree.
- The direction of magnetic field depends upon direction of current in the three-phase stator winding.
- The rotor always tries to keep its position in the direction of strongest magnetic field of stator winding.
Why permanent magnet rotor is not used in
synchro?
- When ac supply is given to stator winding of synchro, direction of pole reverses during positive and negative half cycle of stator supply.
- The direction of stator pole reverses during negative half cycle of alternating supply, it will result in rotor or permanent magnet rotates at 180 degree.
- The rotor again rotates at 180 degree again during positive cycle of alternating supply but rotor does not rotate quickly in the direction of magnetic field due to inertia of rotor.
- Due to low torque on rotor, a permanent magnet is not used in the rotor.
Now, we will
understand the direction of rotation of rotor.
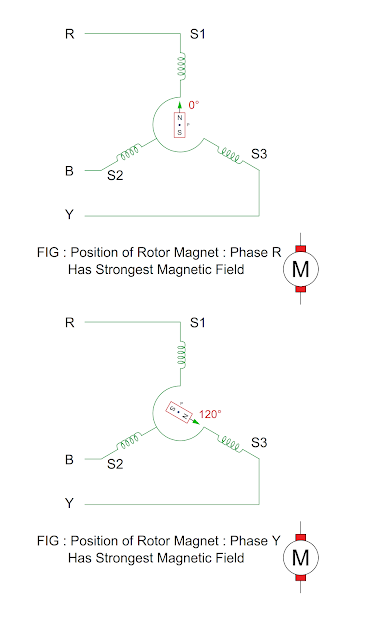
Point a
- As the magnetic field of phase R is strongest, the rotor rotates in the direction of magnetic field of phase R.
- As the direction of stator magnetic field and rotor magnetic field is same, it is called as zero electrical position.
Point b
- As the magnetic field of phase Y is strongest, the rotor rotates in the direction of magnetic field of phase Y or 120 degree in the clockwise direction.
Point c
- As the magnetic field of phase B is strongest, the rotor rotates in the direction of magnetic field of phase Y or 240 degree in the clockwise direction from its initial position.
- The direction of magnetic field of rotor depends upon magnetic field strength.
- The rotor rotates in the reverse direction if the direction of current is reversed in the stator.
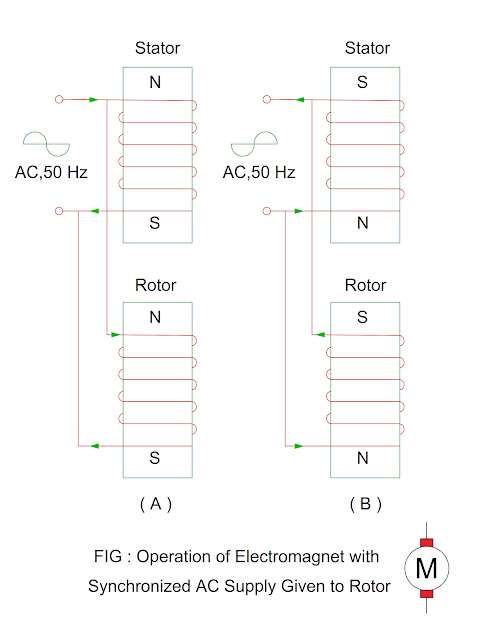
Why the stator and rotor of the synchro
operates with alternating supply?
- The direction of stator and rotor magnetic field simultaneously changes when it is operated by alternating supply.
- The force of attraction between stator pole and rotor pole during positive half cycle of alternating supply.
- Similarly, the direction of stator magnetic field and rotor magnetic reverse simultaneously during negative half cycle of alternating supply.
|
You may
also like to read How to reduce
mitigation of third harmonics? Effect of
harmonics on power factor What do you mean
by current harmonics and voltage harmonics? |
Download Power Point : Synchro - Construction, Working & Applications









No comments:
Post a Comment