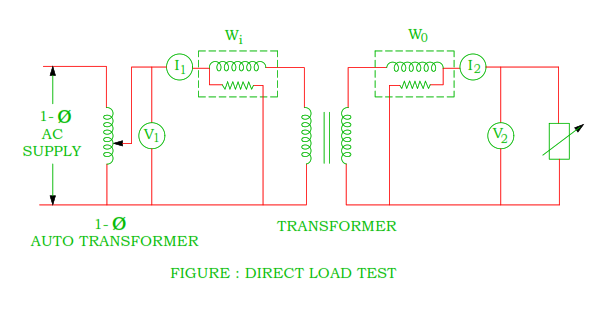
- The circuit diagram for the direct loading test is shown in the figure.
- As the transformer is loaded, this test is known as direct test. The rated voltage is given to transformer primary side with the help of single phase auto-transformer and secondary side is loaded.
- The load is increased step-by-step till ammeter A2 shows the full load secondary current. Note down the reading of wattmeter, voltmeters and and ammeters.
|
Primary
Voltage |
Primary
Current |
Input
Power |
Secondary
Voltage |
Load
Current |
Output
Power |
|
V1 |
I1 |
WI |
V2 |
I2 |
W0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Efficiency
%
Efficiency = [ Output Power / Input Power ] × 100%
= [ W0 –
WI ] × 100%
Voltage
Regulation
Let
us consider that no load secondary voltage is 0V2 and
full load secondary voltage is V2
% Voltage
Regulation = { NLSV – FLSV / NLSV } × 100 %
= { 0V2 –
V2 / 0V2
}× 100 %
Where
NLSV = No load
secondary voltage
FLSV = Full
load secondary voltage
Advantages
- It is accurate method.
- As the transformer is loaded, heating condition is known at different load current.
Disadvantages
- This test is applicable only for small kVA transformer because it is very difficult to arrange large load for medium and high capacity transformers.
- Wastage of power is done in the external load circuit
What is effect of load current on efficiency and voltage
regulation of transformer?
- The efficiency increases up to full load current and its value slightly decrease for overloaded condition.
- As the load current increases, the voltage regulation is also increased.
- It should be noted that the voltage regulation of the transformer depends on both the load current and power factor of the load.
You may also like :
Tertiarywinding : Construction and Working
Earthing
Transformer : Construction and Working
Hysteresis
Motor : Construction, Working, Characteristic, Applications
Reluctance
Motor : Construction, Working, Characteristic, Applications








No comments:
Post a Comment