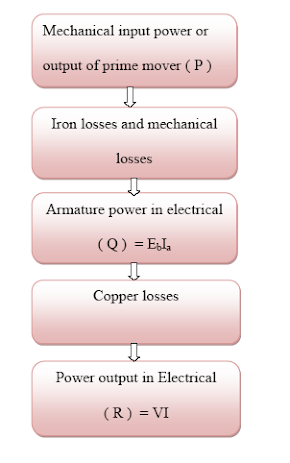
The power stages of DC Generator is shown in the Figure
Commercial Efficiency
- It is defined as the ratio of the electrical power output to the mechanical power input.
ηc = [ Electrical power input ] × 100% / [
Mechanical power input ]
Mechanical Efficiency
- It is defined as the ratio of the armature power to the mechanical power input.
ηm = [ Armature power ] × 100% / [ Mechanical
power input ]
Electrical Efficiency
- It is defined as the ratio of the output power in mechanical to the armature power.
ηe = [ Output power in mechanical ] × 100% / [ Armature
power ]
Condition For Maximum Efficiency
Generator output power = VIL
Generator input power = Output power + Total losses
= VIL + Constant losses + Copper losses
= VIL + WC + Ia2Ra
= VIL + WC + ( IL + Ish
)2 Ra
The value of shunt field current is very small as compared to
load current therefore the shunt field current is neglected.
Generator input power = VIL + WC + ( IL
)2 Ra
Generator efficiency = Output power / Input power
= VIL / VIL + WC + ( IL )2
Ra
= 1 / [
1 + ( WC / VIL2
+ IL Ra
/ V ) ]
The load current is variable parameter therefore the
generator efficiency becomes maximum when
dη / dIL = 0
d / dIL [( WC / VIL2 + IL
Ra / V ) ] =
0
( WC / V ) ( 1 / – IL2 ) + (
Ra / V ) ( 1 ) = 0
IL2 Ra = WC
Therefore the variable losses is equal to constant losses is
condition for maximum efficiency in the DC Generator.
IL2 Ra = WC
Load current for maximum efficiency
IL
= √ ( WC / Ra )
You may also like :
Compare Capacitor bank and Individual capacitor
Effect of harmonics on power factor
What do you mean by Current harmonic and Voltage harmonic?








No comments:
Post a Comment