In this theory,
cut off region, active region and saturation region of the transistor is
explained.
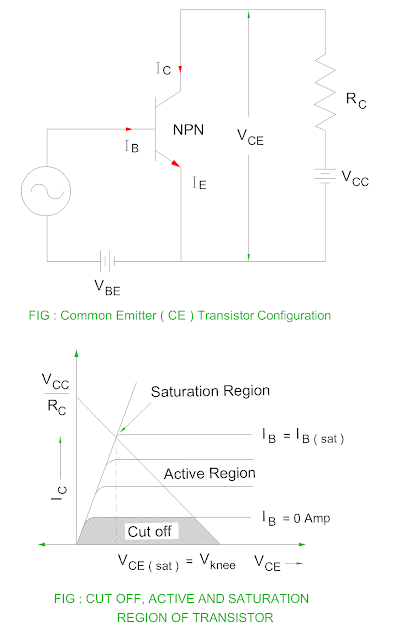
Active Region, Cut off Region and Saturation Region of Transistor
Cut off region of Transistor
- When load line intersect IB = 0, it is known as cut off region of the transistor.
- As the base current is zero, only small collector leakage current flows. The base emitter junction does not remain in the forward biased because the base current is zero.
- The collector to emitter voltage is equal to VCC.
Saturation Region of Transistor
- When the load line intersect IB = IB ( saturation ) , it is known as saturation region of the transistor.
- As the base current is maximum, the collector current also becomes maximum.
- The collector to emitter junction does not remain in the reverse biased condition therefore the transistor action is also lost.
- If the base current increases beyond saturation level, the collector current does not increase because of collector to base junction is not remain reverse biased.
IC =
VCC / RC
Active Region of Transistor
- It is a region between active and cut off of the transistor output characteristic.
- The base to emitter junction remains in forward biased condition whereas the collector to emitter junction remains in the reverse biased condition.
Current During Different Region of Transistor
Active region
Collector
current IC = βIB
- The transistor works as an amplifier in the active region
Cut off region
- As there is no base current, the collector current also becomes zero.
Saturation
region
Region
|
Base
– emitter diode
|
Emitter
– collector diode
|
Cut
off
|
OFF
|
OFF
|
Saturation
|
ON
|
ON
|
Active
|
ON
|
OFF
|
You may also
like :








No comments:
Post a Comment