Single Phase unexcited Synchronous Motor
- The characteristic of single phase unexcited synchronous motor in which excitation does not necessary is given below.
( 1 ) It operates on
single phase supply.
( 2 ) The stator rotating magnetic field rotates at synchronous speed.
( 4 ) It is self starting.
Reluctance Motor
Principle
- When a magnetic material is placed in the magnetic material, it always aligns in the minimum reluctance path.
Construction
Stator
- The stator of the reluctance motor is similar to that stator of the single phase induction motor.
- It consists of starting and running winding in the stator slots.
- This type of motor is also called as Split phase reluctance motor.
Rotor
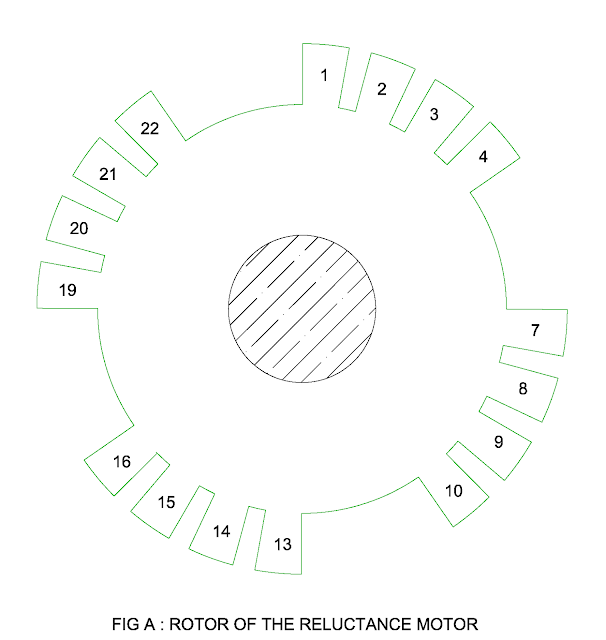
- The rotor of the reluctance motor is of salient or projecting poles.
- Let us consider that the rotor of the squirrel cage induction motor consists of 24 copper bars.
- If the rotor bar 5, 6, 11, 12,17,18,23 and 24 are cut, it is similar to 4 salient poles.
Working
- When a single phase supply is given to the stator winding, a rotating magnetic field is produced in the stator winding.
- When a salient poles rotor cut this magnetic field, rotor aligns in the minimum reluctance path due to reluctance torque.
- The reluctance depends upon air – gap between stator and rotor.
- Figure A shows 4 pole salient pole rotor in which direction of four high Permeance and four low Permeance is shown.
- High Permeance means higher magnetic conductivity and higher inductance. Similarly low Permeance means lower magnetic conductivity and lower inductance.
- The reluctance is inverse of Permeance. Low reluctance means higher inductance and vice versa.
L α N2
/ S
Where L =
Inductance and
S = Reluctance of magnetic path
- Low air – gap means low reluctance and vice versa
S = L / μ0μra
Where L = Length
of air – gap
μ0 =
Absolute permeability = 4π × 10 – 7 Henry / meter
μr = Absolute permeability
a = Area
- There is low reluctance path between stator and salient poles due to small air – gap whereas high reluctance path between stator and inter – polar axis due to large air – gap.
- The reluctance motor starts as an induction motor.
- When the rotor rotates at its maximum speed, it aligns with the stator synchronous magnetic field due to reluctance torque.
- The angle between stator poles and rotor poles of opposite polarity is called as torque angle.
- As the torque angle increases, the reluctance torque also increases.
- The maximum reluctance torque attains at torque angle of 450.
- The load taken by the reluctance motor is only fraction of the load taken by the three phase inductance motor.
Advantages
- Low maintenance
- DC supply not necessary
- Simple construction
- Constant speed characteristic
Disadvantages
- Low efficiency
- Low power factor
- Only fraction of load taken as compared to three phase induction motor
Applications
- Automatic regulator
- Signaling devices
- Recording instruments
- Tele printer
- Timer circuits
- Gramophone
You may also like :








No comments:
Post a Comment