Charge
and Current
- The law of
conservation of energy states that the charge can neither created nor destroyed,
it can only transferable from one place to another place.
- Therefore the
algebraic sum of all charge in an electrical circuit is equal to zero.
- The
electrical charge is mobile therefore it can be transferred to one place to
another.
- The positive charge moves in one direction whereas the negative charge
moves in the other direction.
- The motion of electrical charge creates
electrical current in a closed circuit.
- The Benjamin Franklin invented that the
conventional direction of electrical current is opposite to negative charge or
electron.
- There is a following relation between charge and current
i = dq / dt
Direct Current (
DC ) or Direct voltage
- If the magnitude of current or voltage does not change with time, it is called as direct current.
- The magnitude of direct voltage and current remains constant with respect to time.
Alternating Current ( AC ) or Alternating voltage
- If the magnitude of current or voltage changes sinusoidal with time, it is called as alternating current.
- The alternating supply may be single phase or three phase.
Voltage or
Potential
- It is defined as
the work done in bringing a positive charge of one coulomb from infinity to
that point against magnetic field.
- The potential is equal to work done per unit
charge.
- The earth is taken as reference potential zero because the potential of
earth remains constant in spite of it keeps and losing charge.
One voltage =
Work done / Charge
- It is force that
requires moving electrons to produce an electrical current. It is better known
as EMF or battery source.
- It is measured in voltage.
- The word force is used for
electrical potential not for mechanical force.
OR
- It is source of
energy that causes electrical current to flow in the given closed circuit.
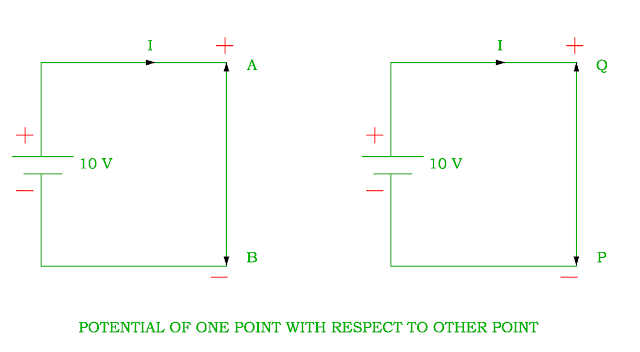
Potential Difference
- It is defined as
potential difference of one voltage between two points if one joule of work is
done for shifting a point charge from one point to other point.
- The potential
difference between two points is considered by considering one point as
reference potential.
- Let us consider that the potential of point is + 10 V as
compared to potential of point B. Similarly the potential of point P is – 10 V
as compared to potential of point Q.